Soda
Soda
 Chlorine Gas
Chlorine Gas
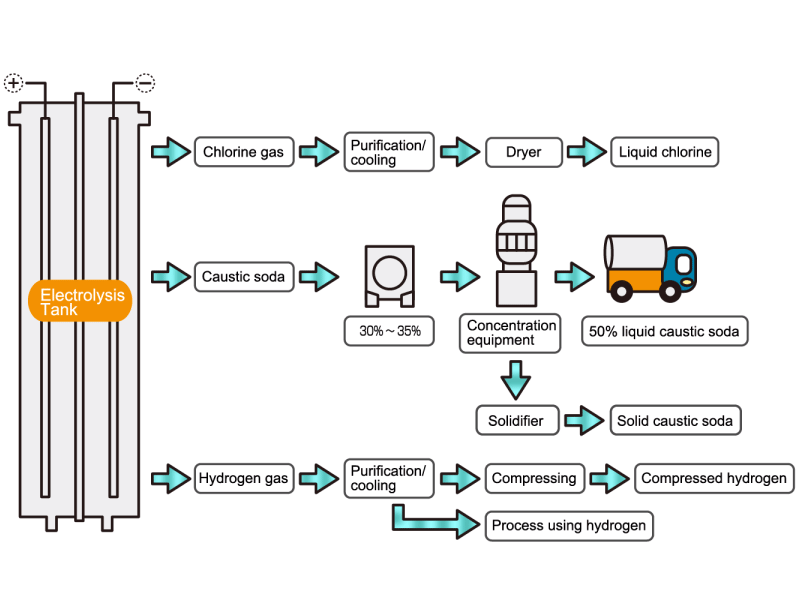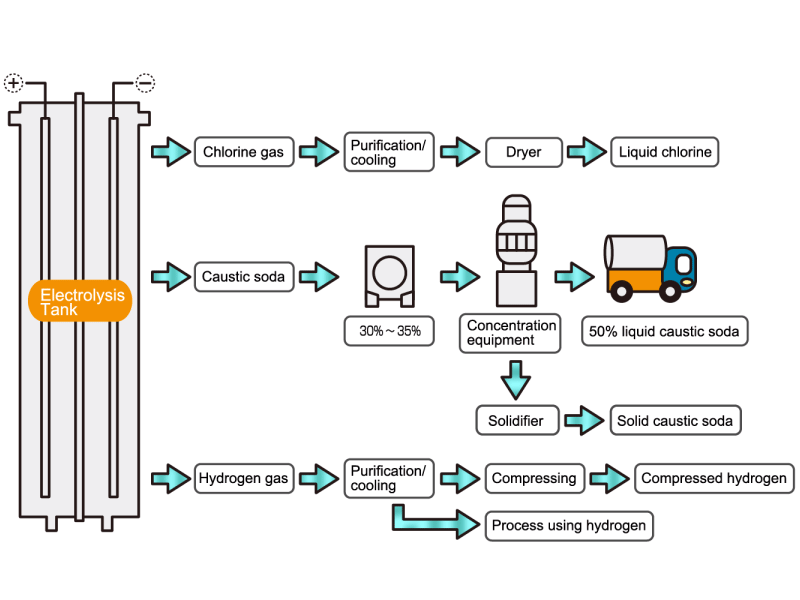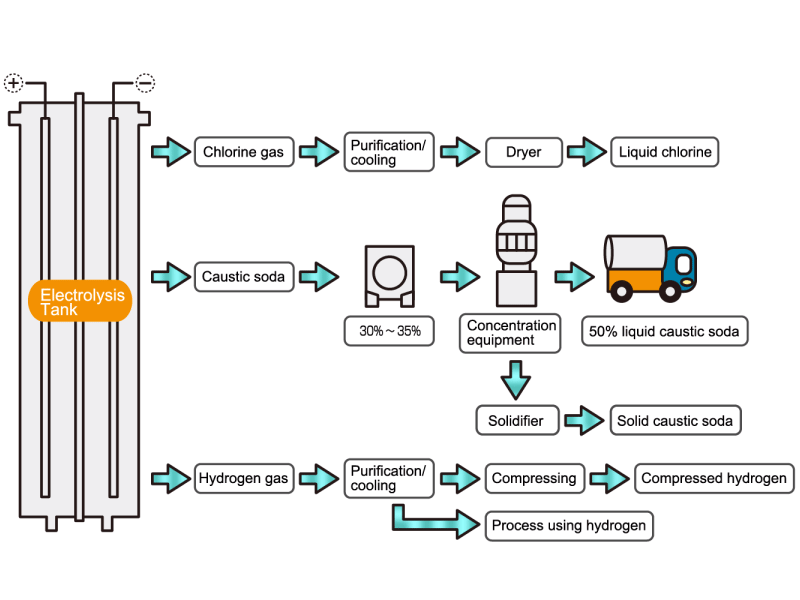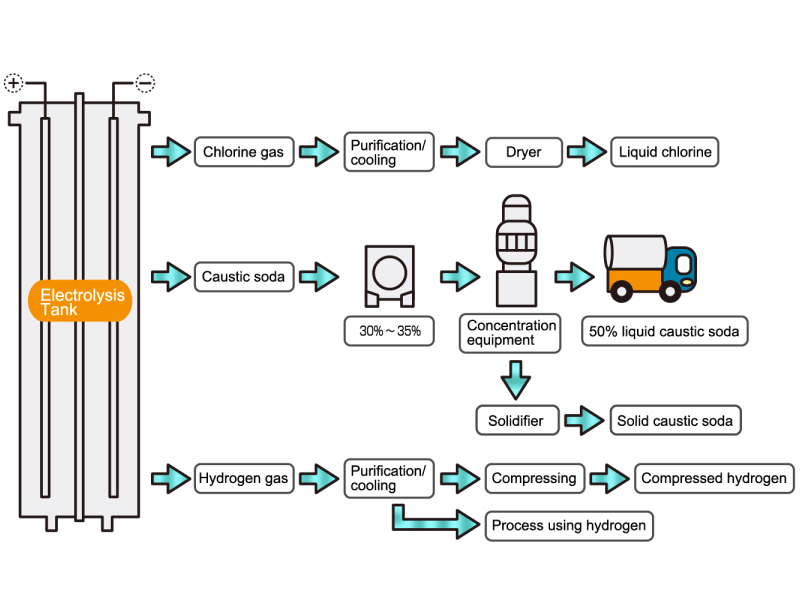
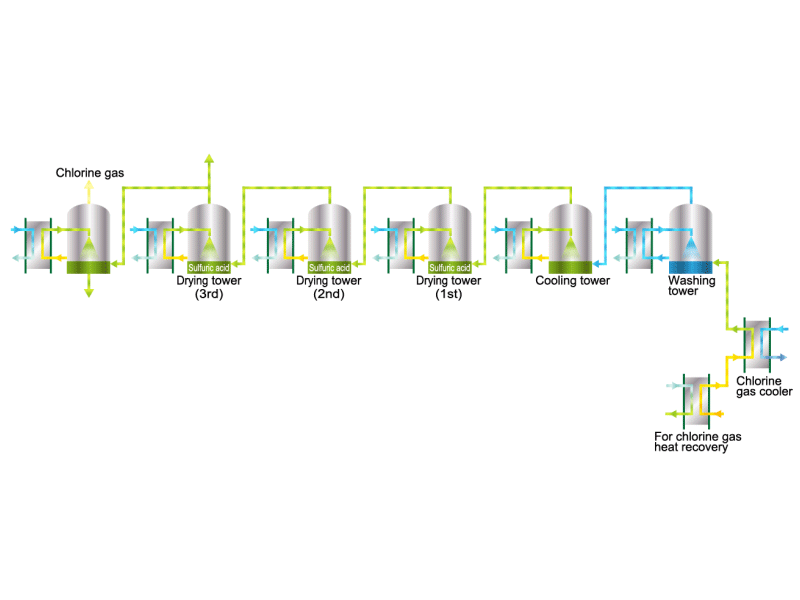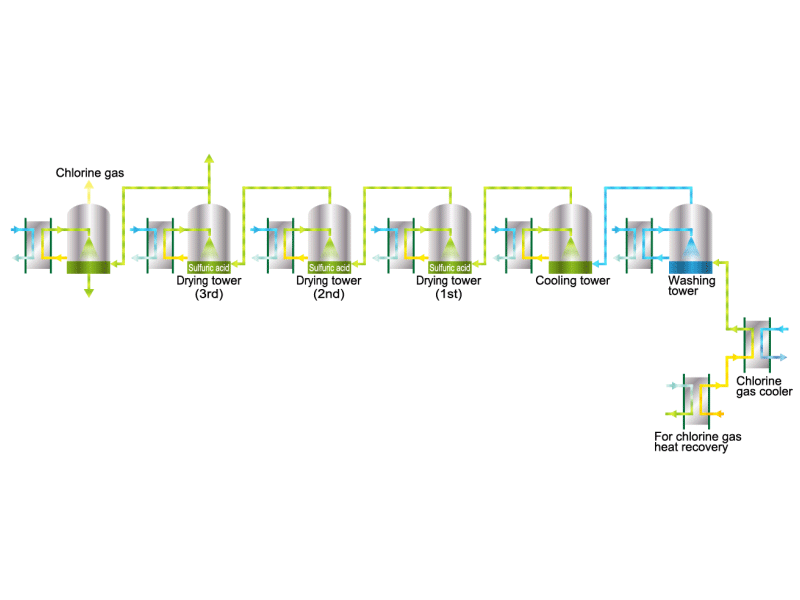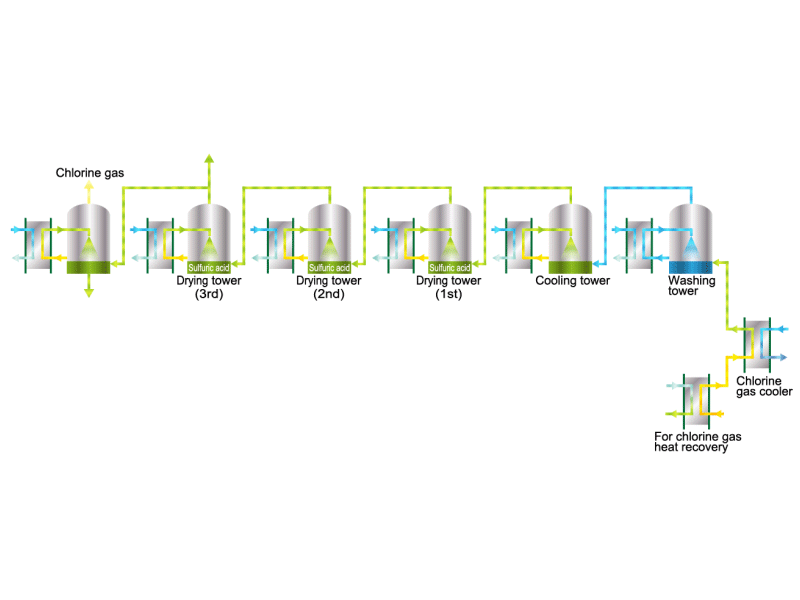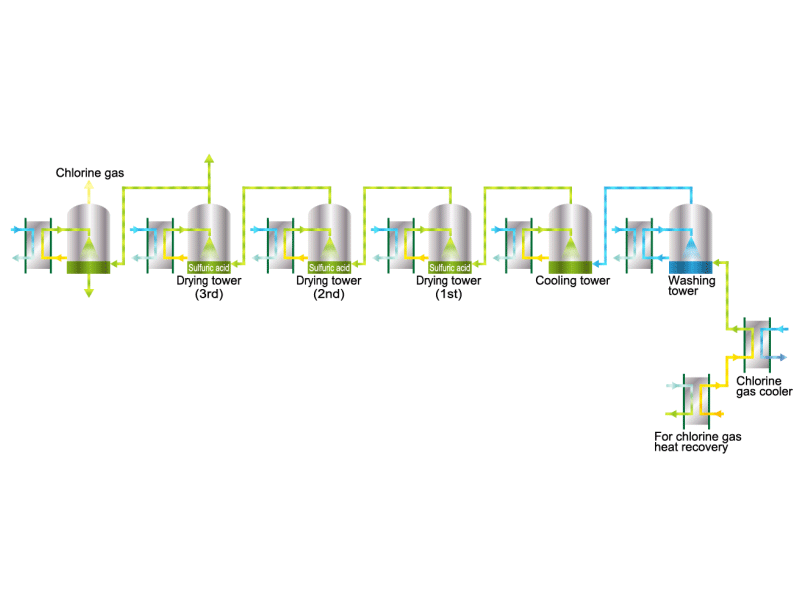
Chlorine gas is generated from electrolytic soda. Since chlorine combines well with other elements, it is used as a raw material for many chemical products, such as a reactant for vinyl chloride resin. HISAKA heat exchangers are used as chlorine gas coolers and coolers for drying columns.
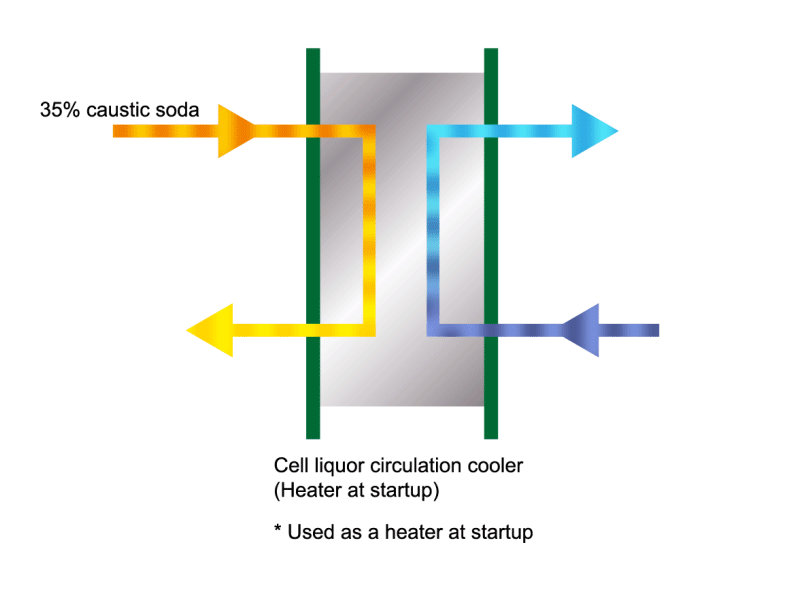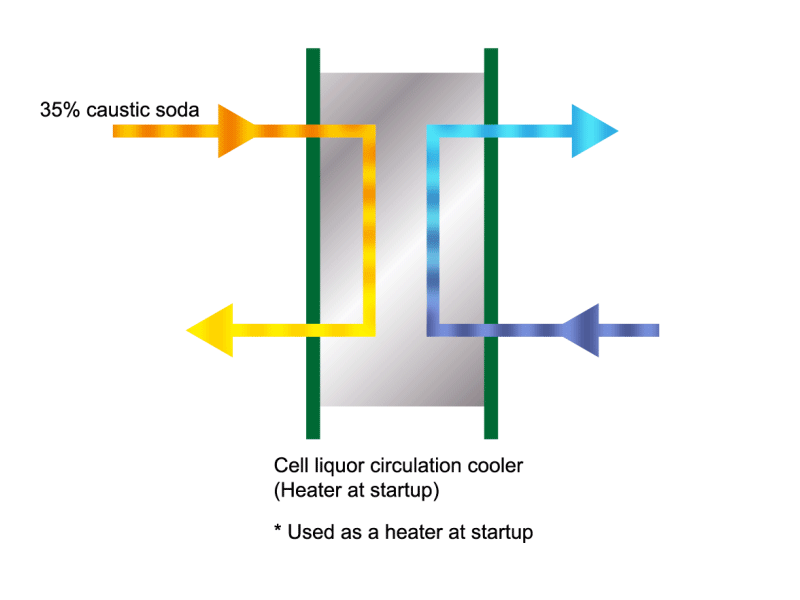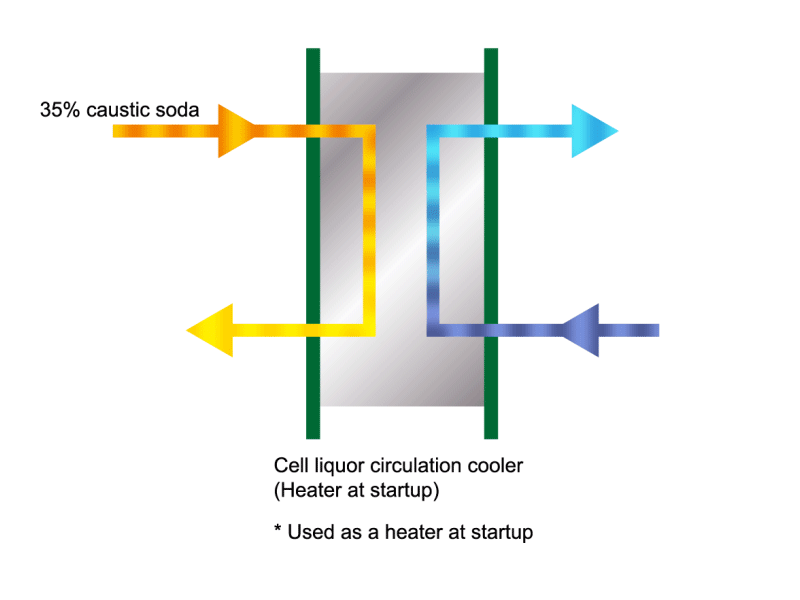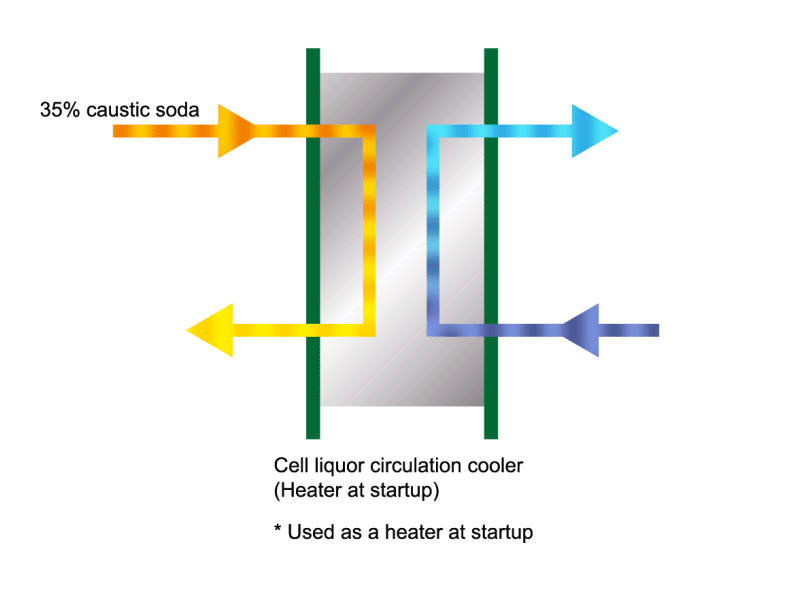
 Caustic Concentration
Caustic Concentration
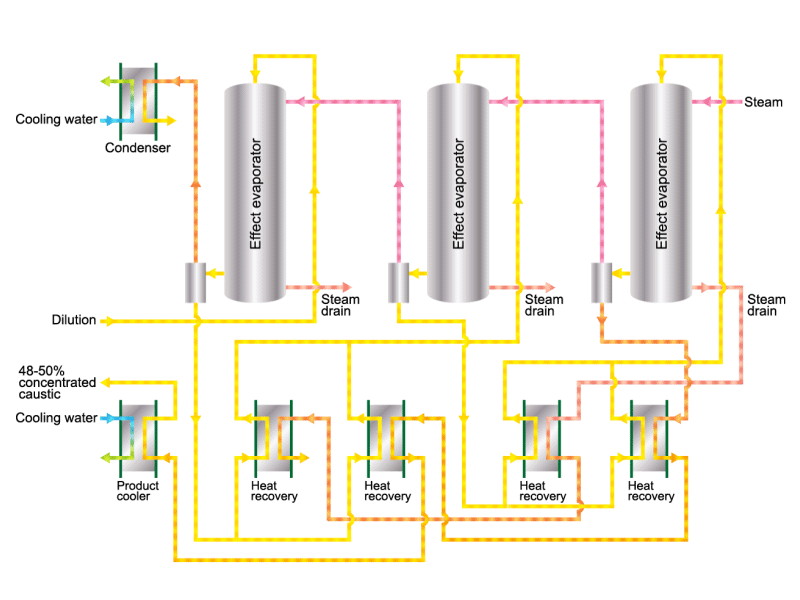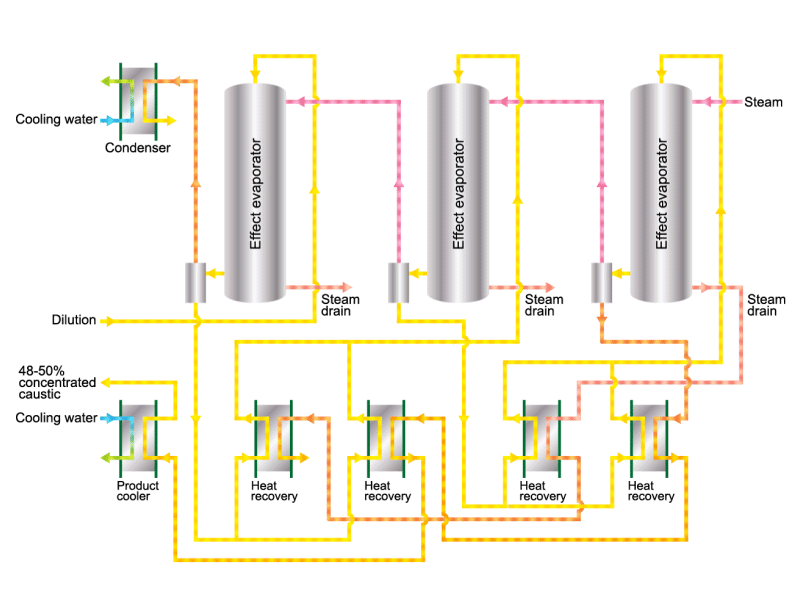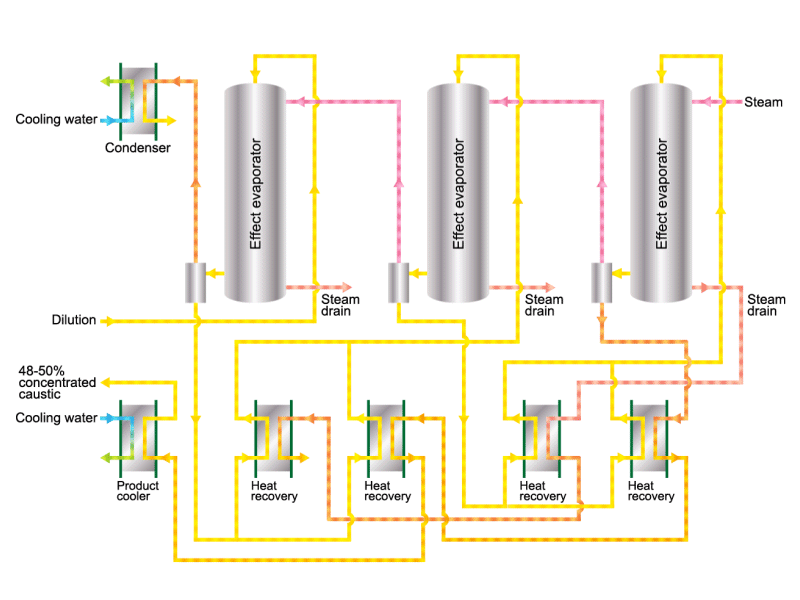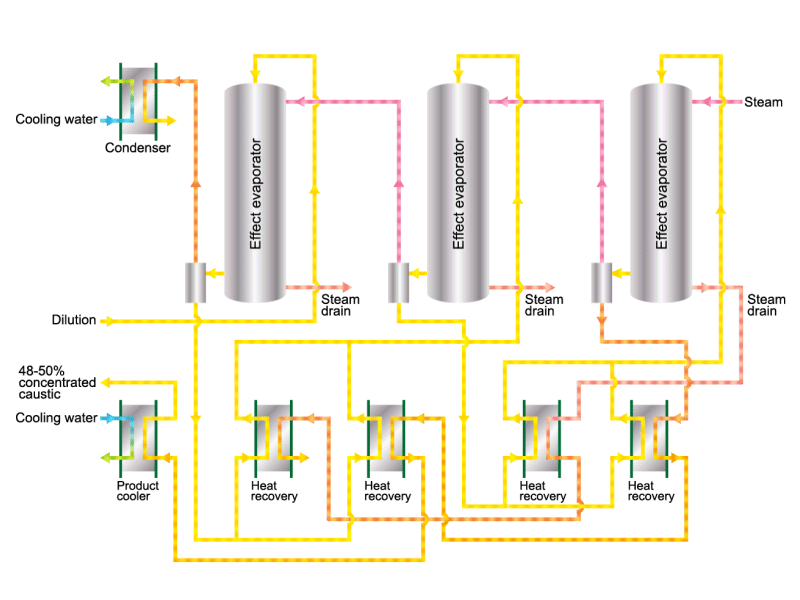
Caustic soda is used in the manufacture of various industrial products, such as a raw material for chemical fibers and detergents, and the bleaching of pulp. Caustic soda is concentrated to about 50% before being shipped. HISAKA heat exchangers are often used in the concentration process.
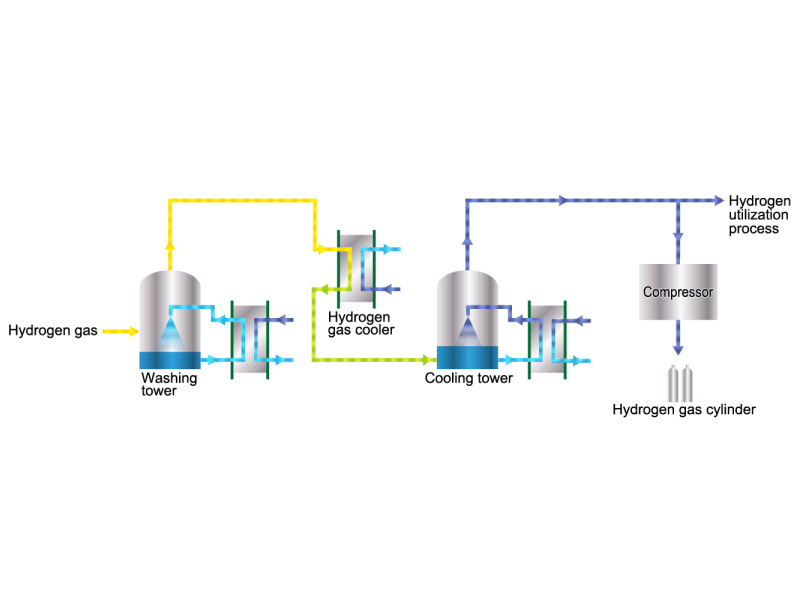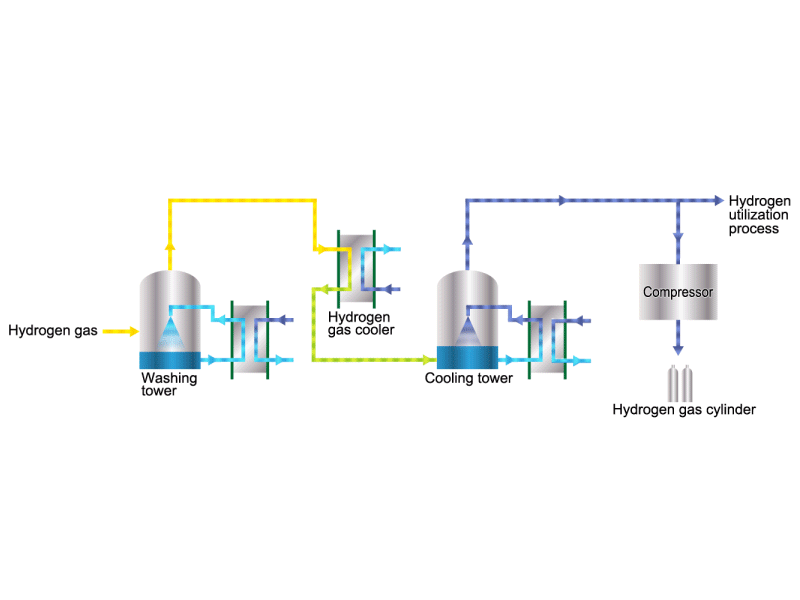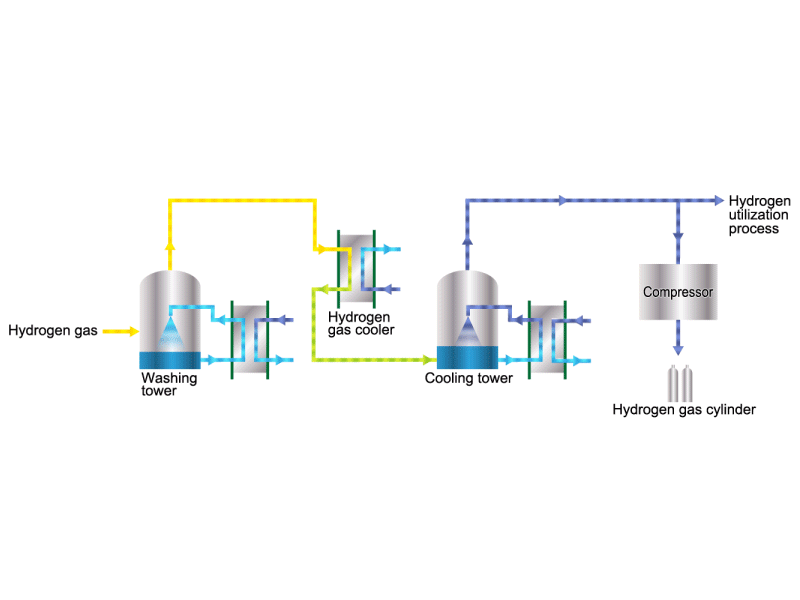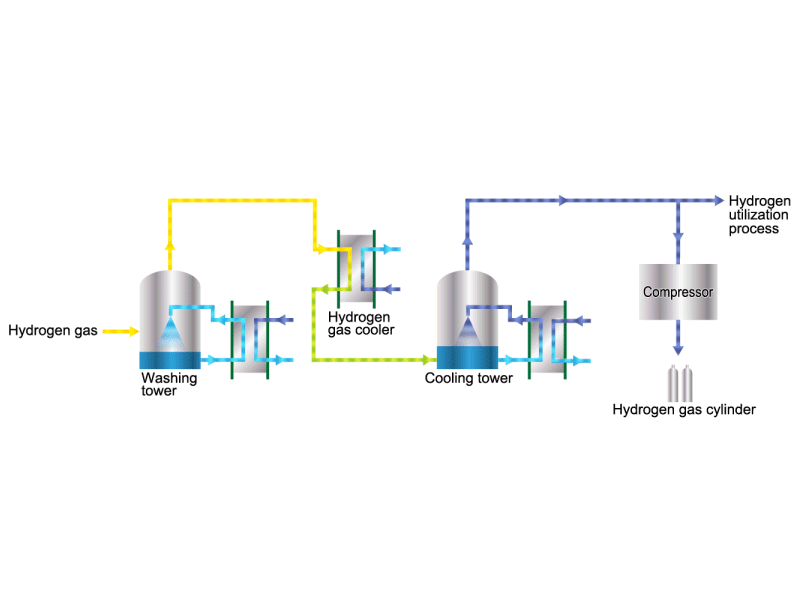
 Hydrogen Gas
Hydrogen Gas
The electrolytic soda industry produces a certain amount of hydrogen gas. After the hydrogen gas is cleaned and cooled, it is either transferred to a manufacturing process that uses hydrogen or packed in a cylinder and shipped as a product. HISAKA heat exchangers are used as hydrogen gas coolers.
 Chlorine (including detoxifying columns)
Chlorine (including detoxifying columns)
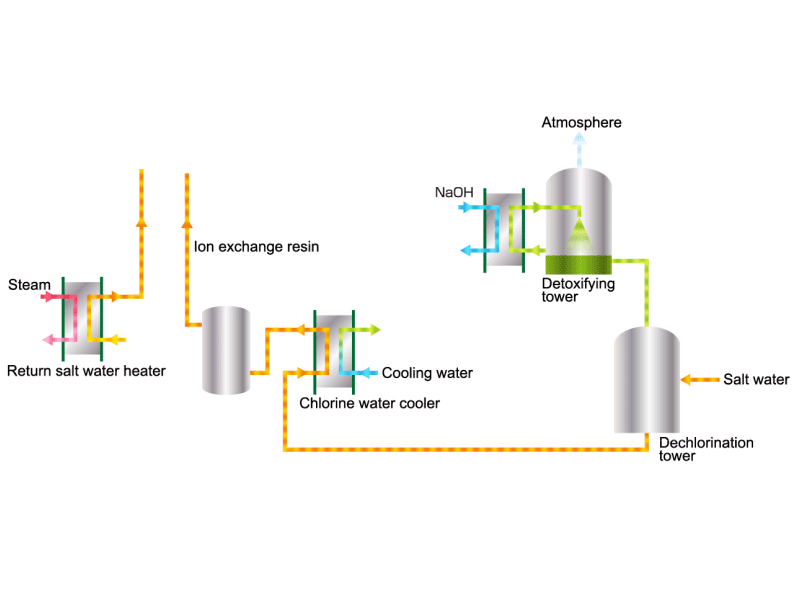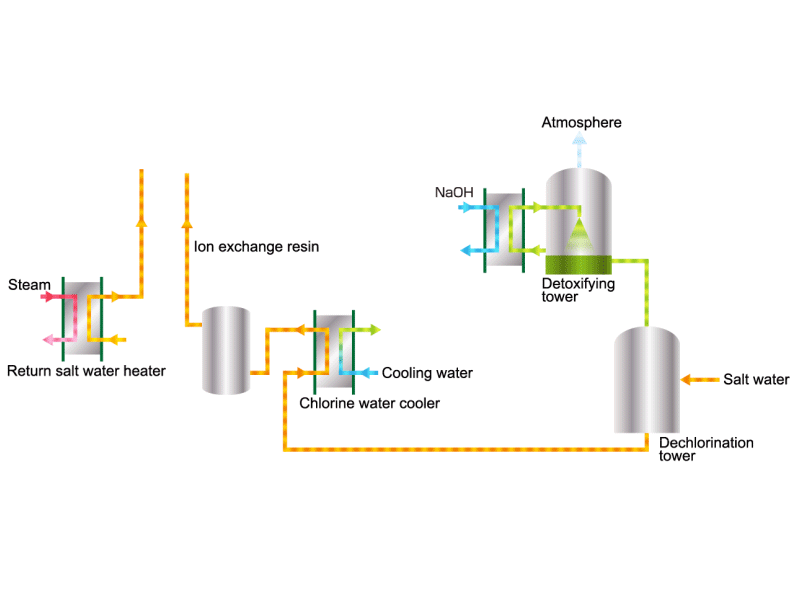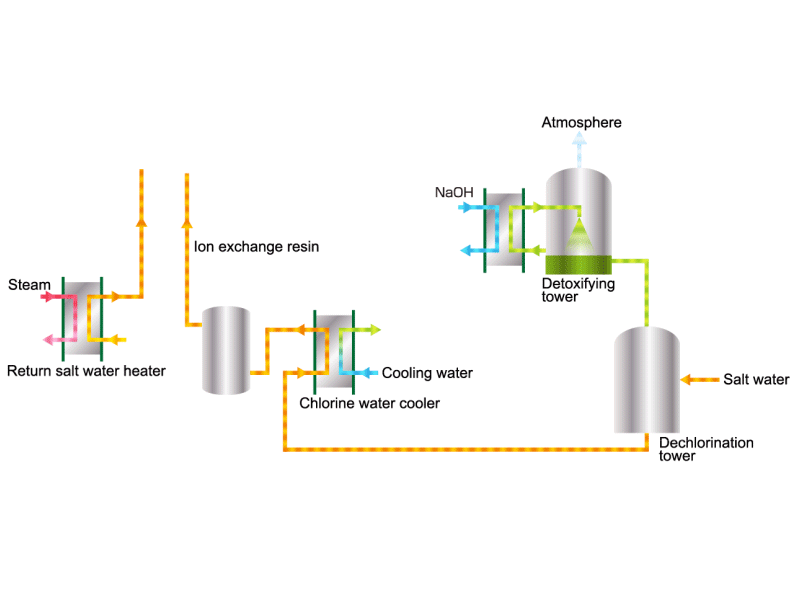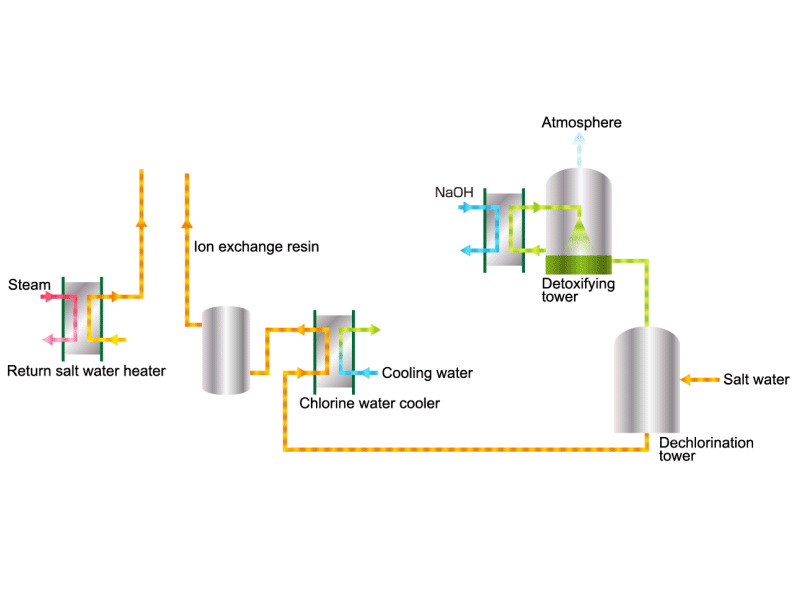
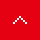
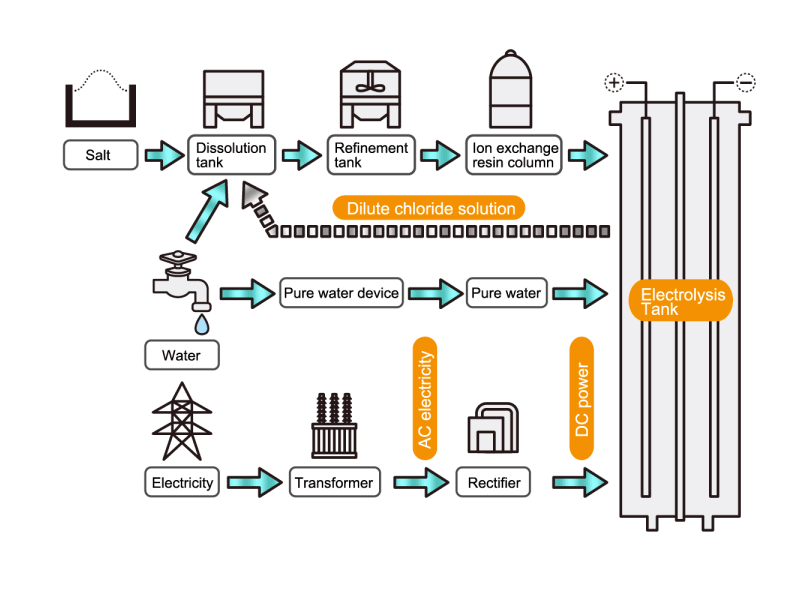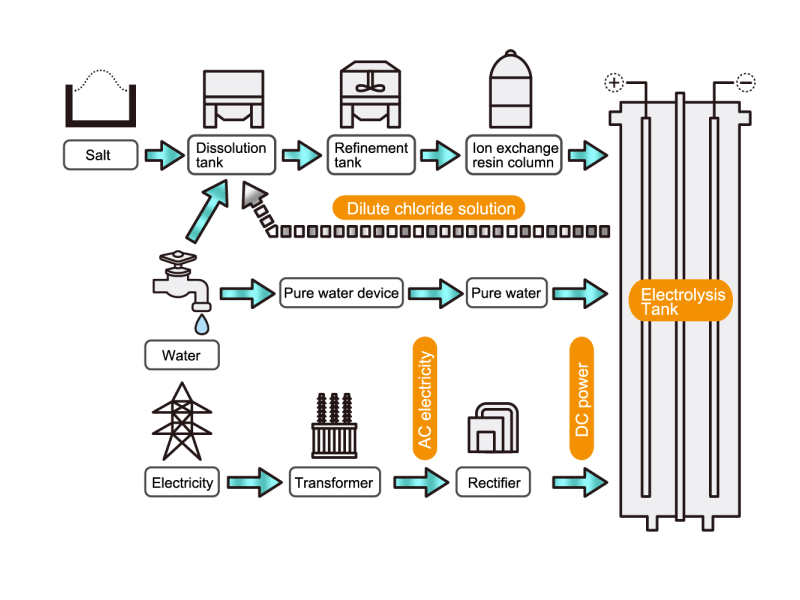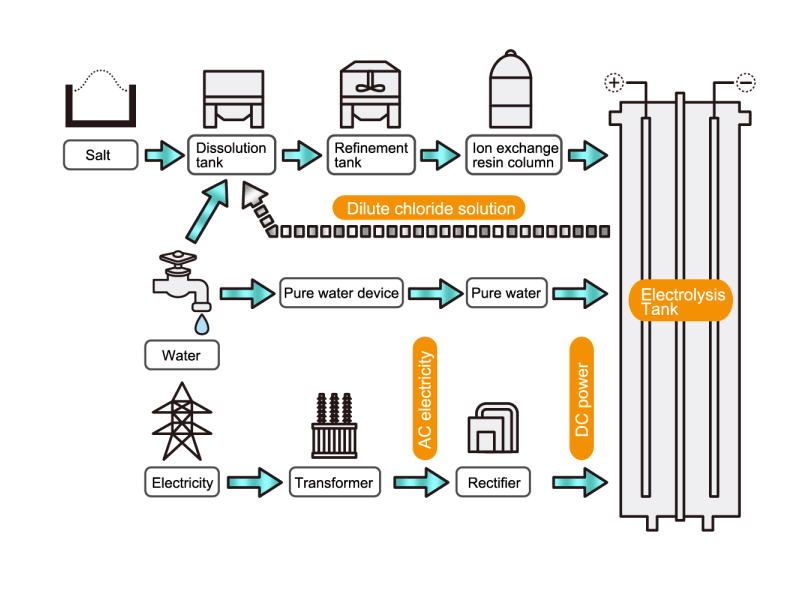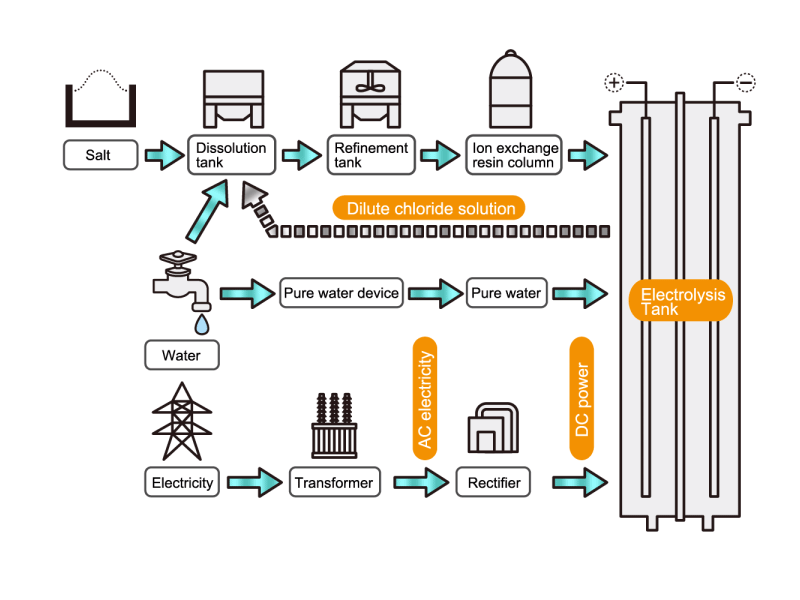
In the electrolysis method, the anode is filled with saline solution and the cathode is filled with water. An electric current is applied, and electrolysis generates chlorine, caustic soda and hydrogen. In this process, HISAKA heat exchangers are used as salt water coolers and coolers for detoxifying columns.