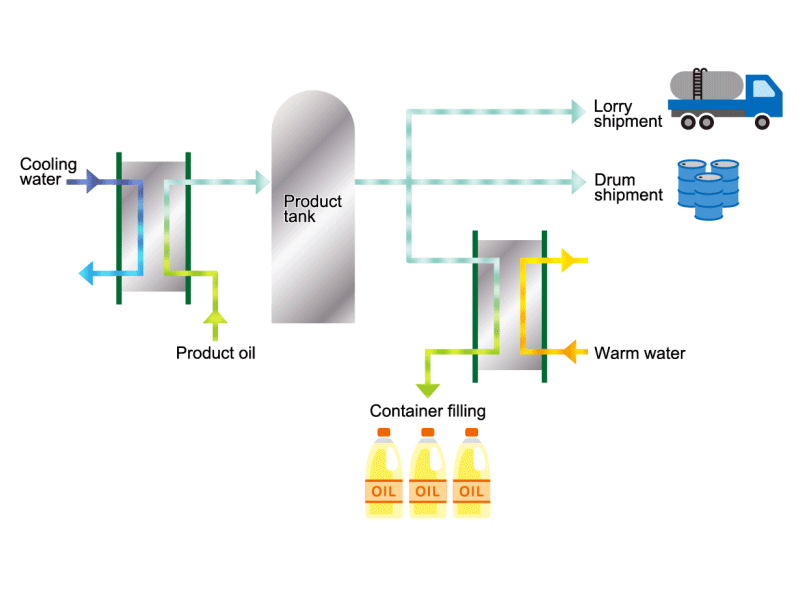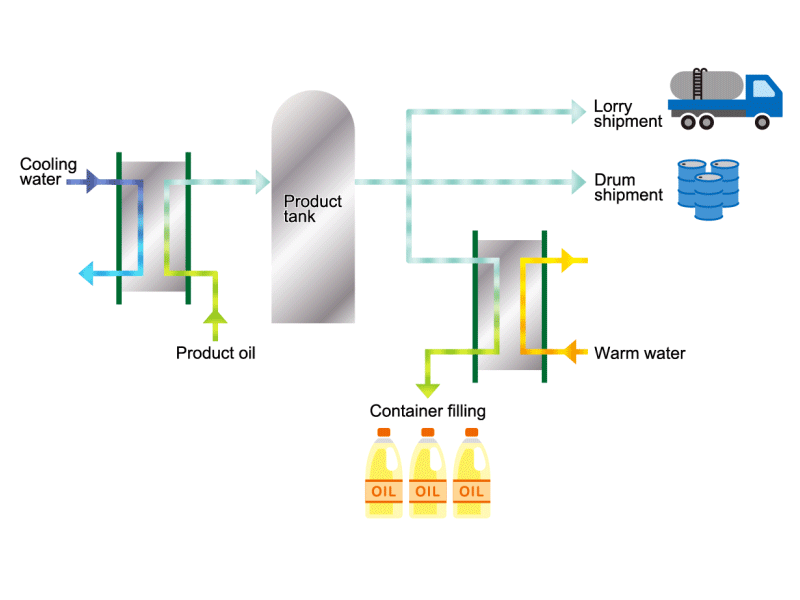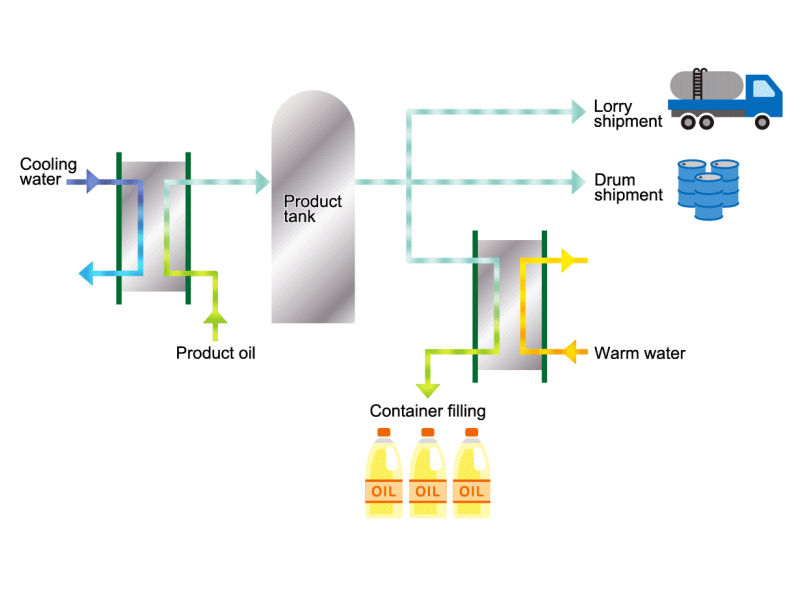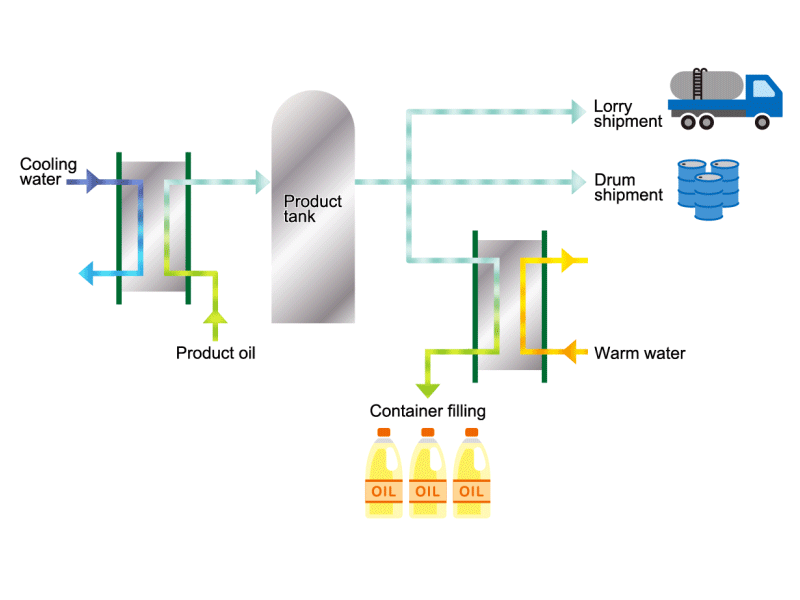
Cooking Oil
Cooking Oil
- Process overview
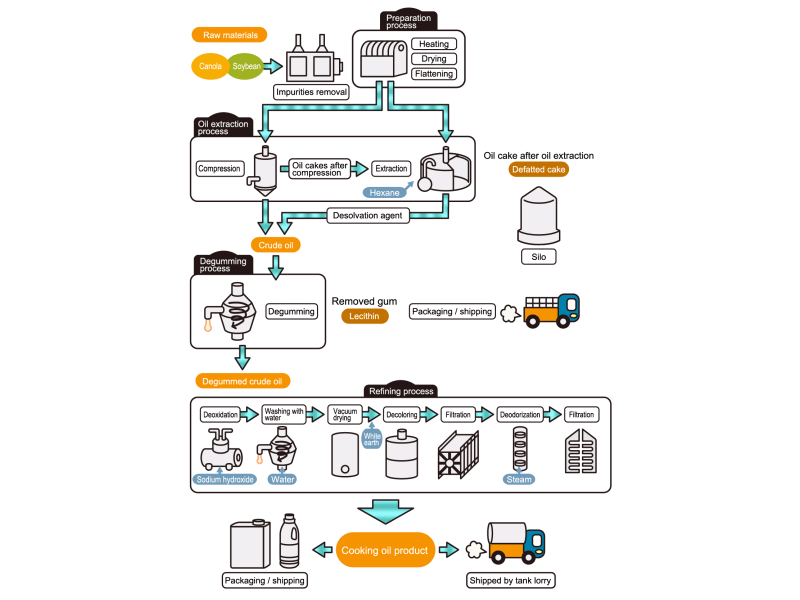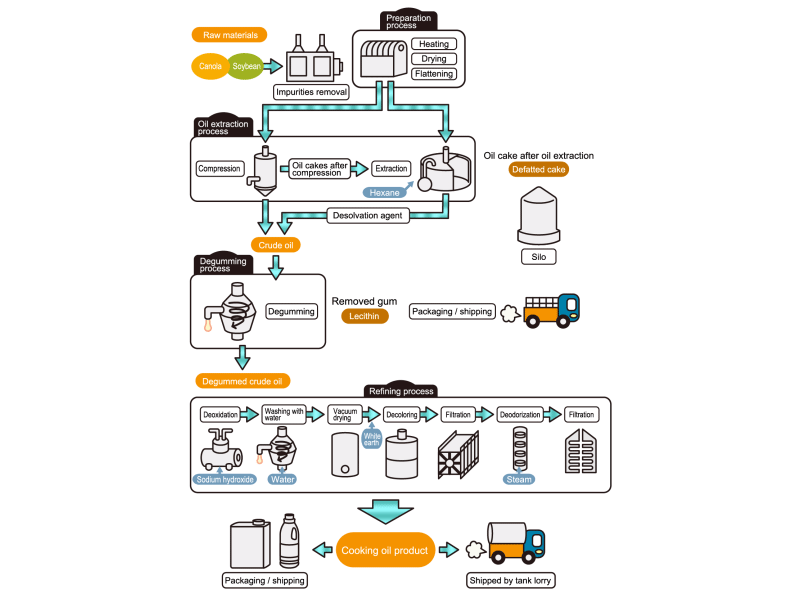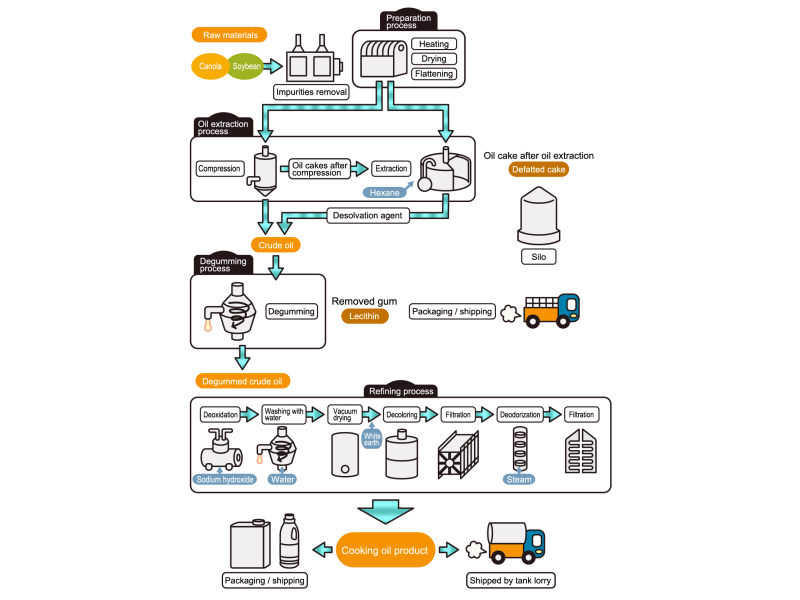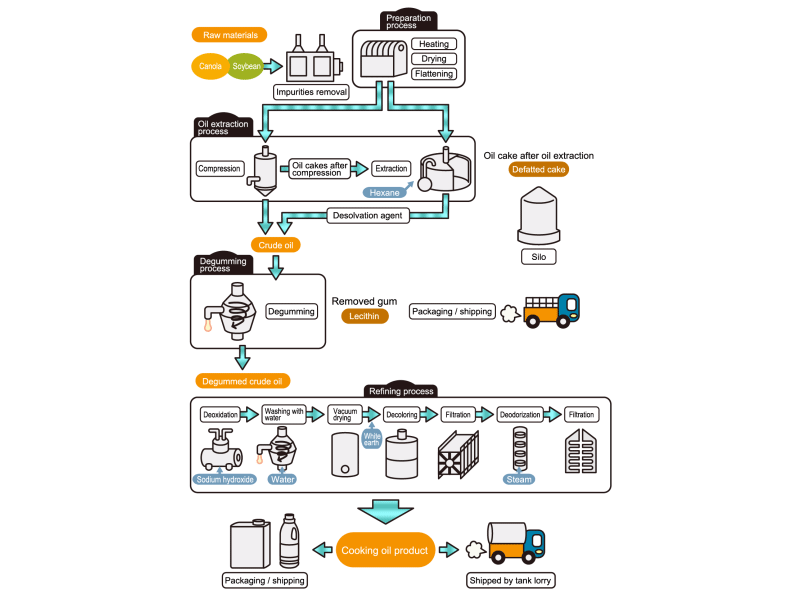
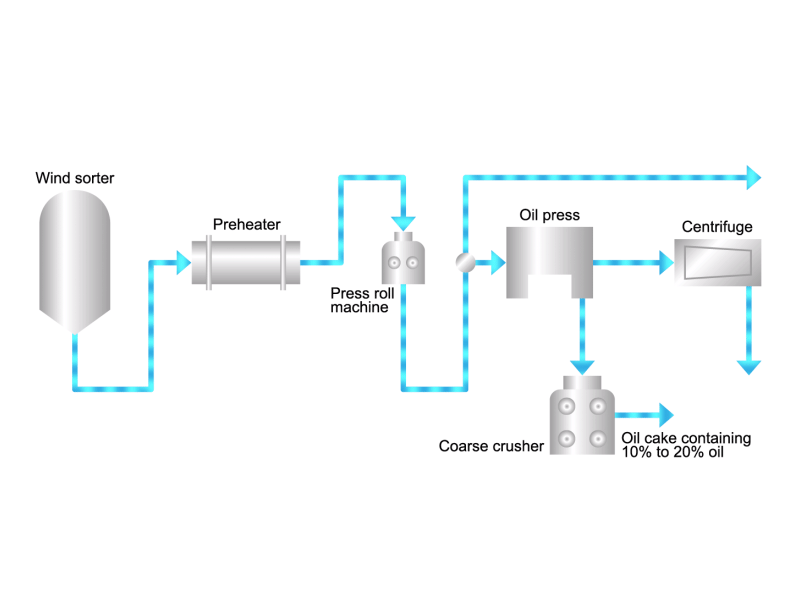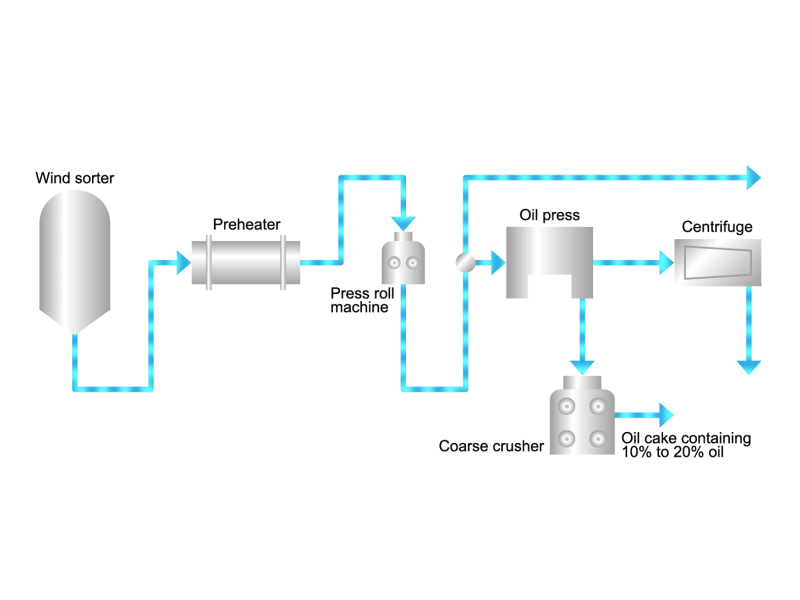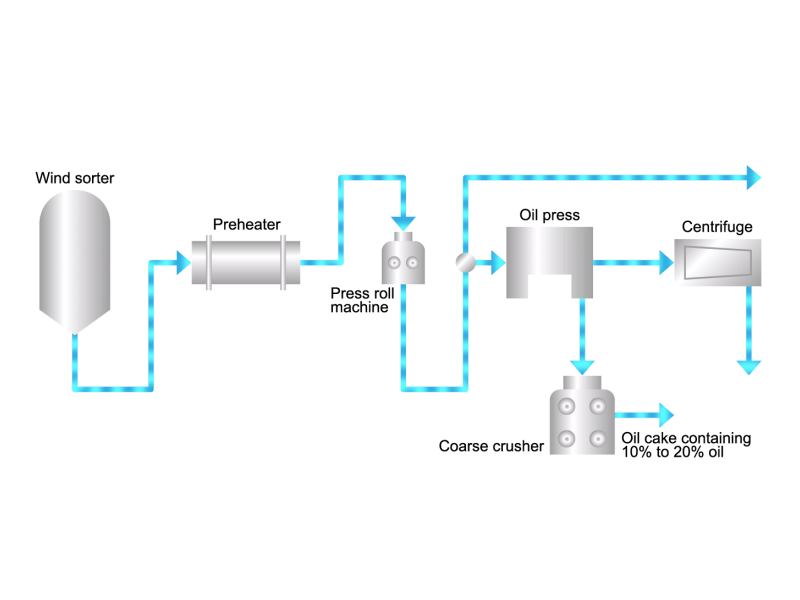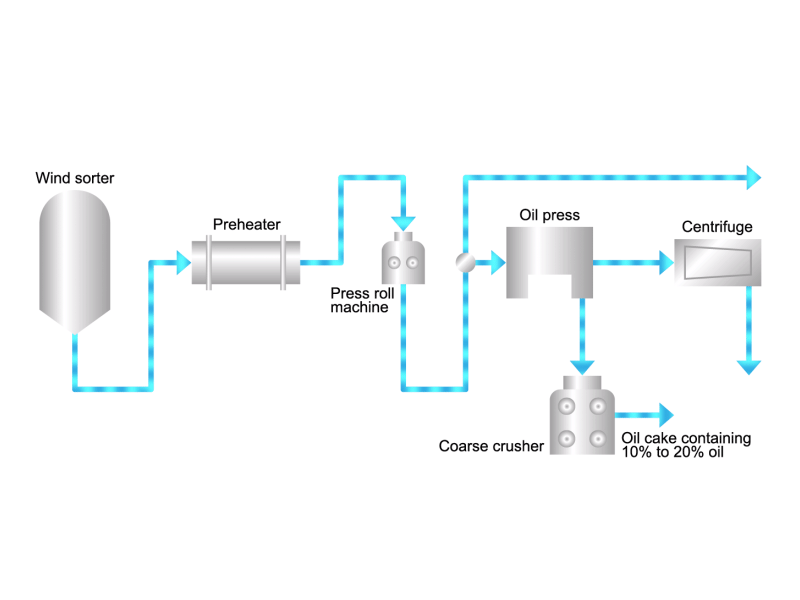
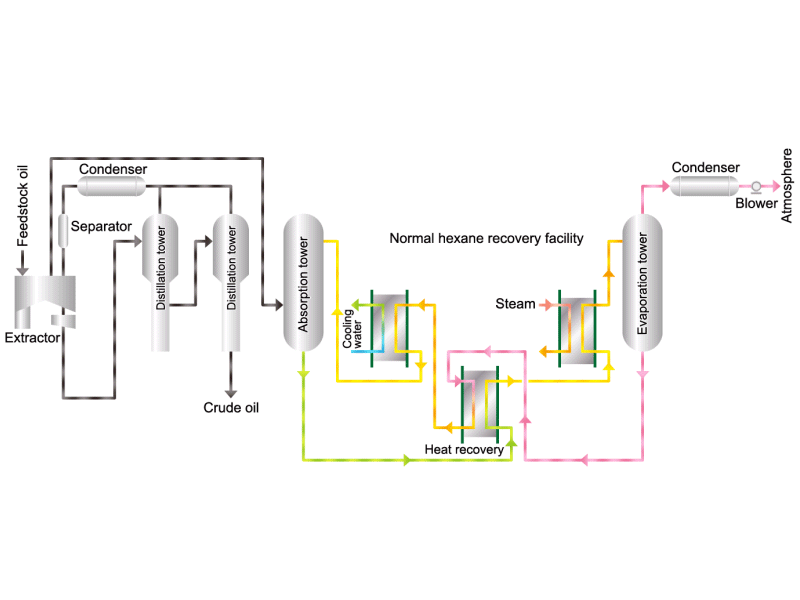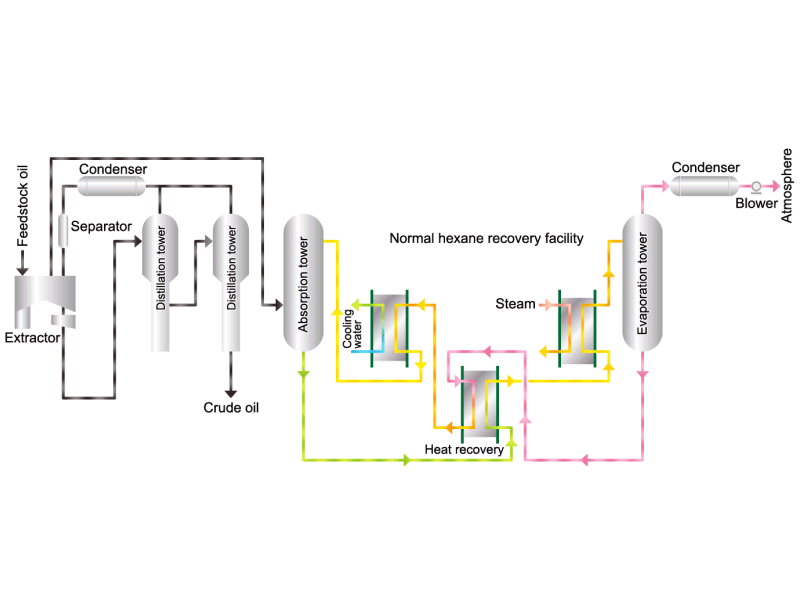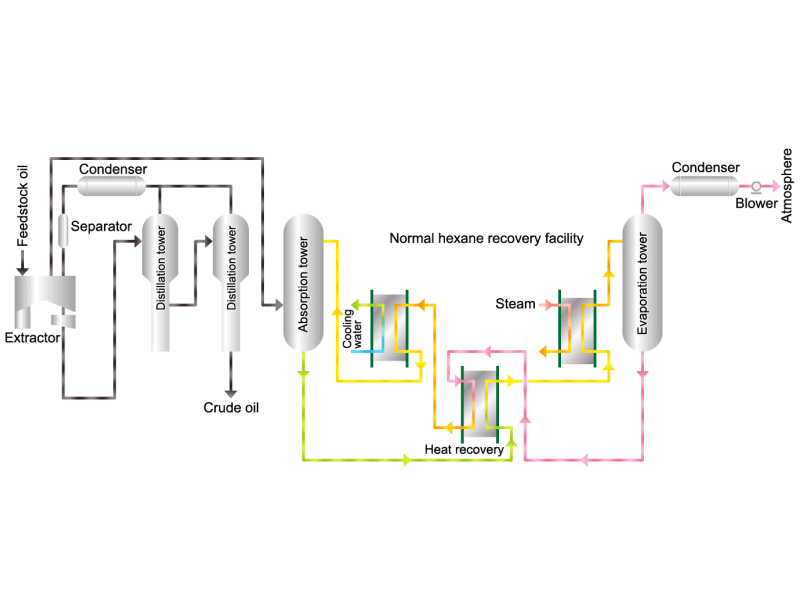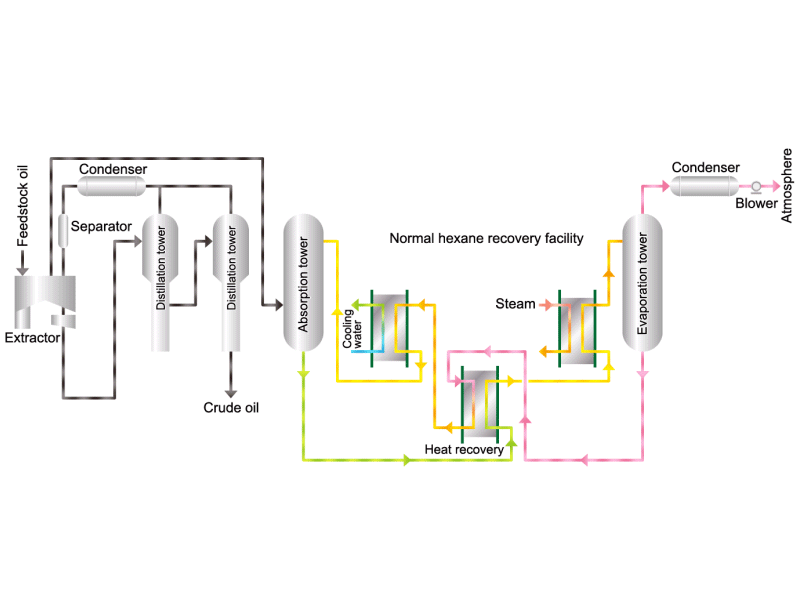
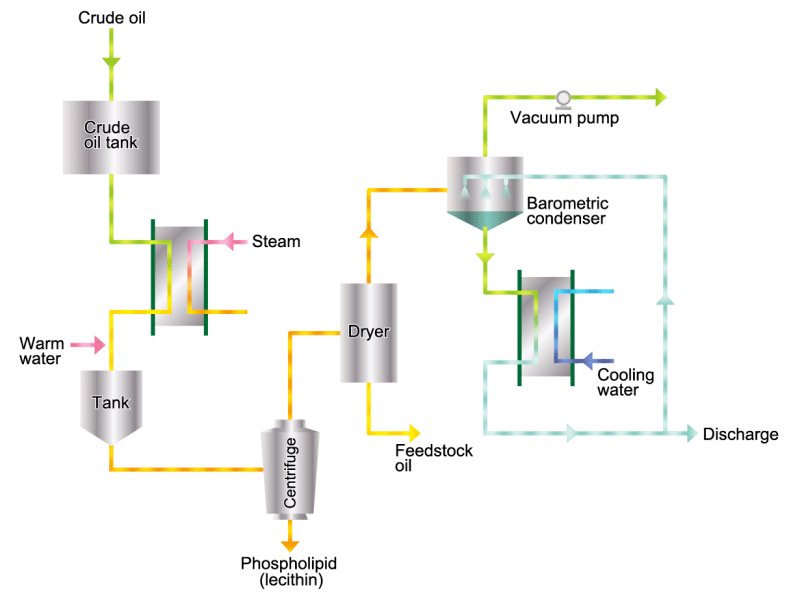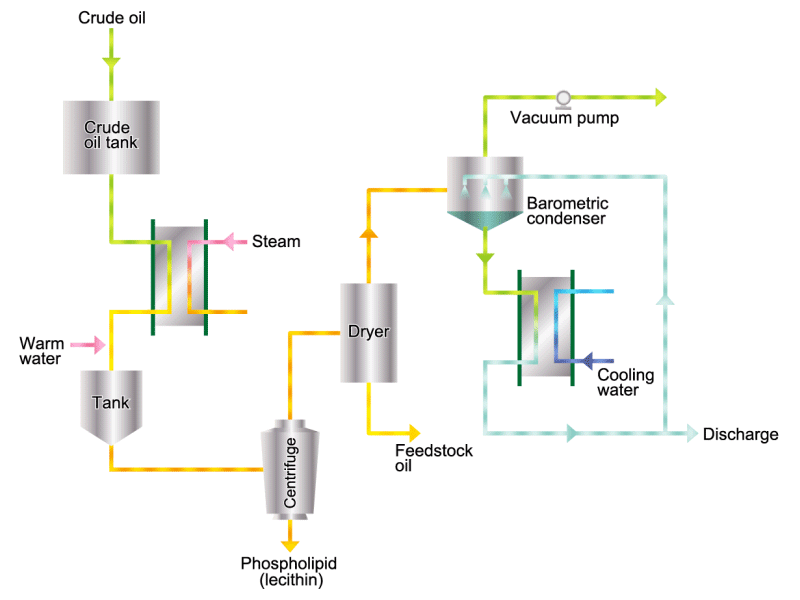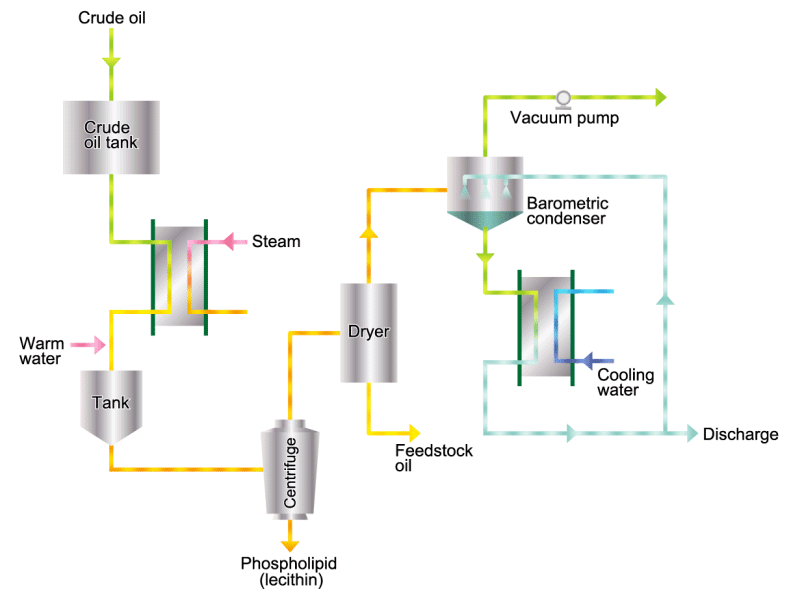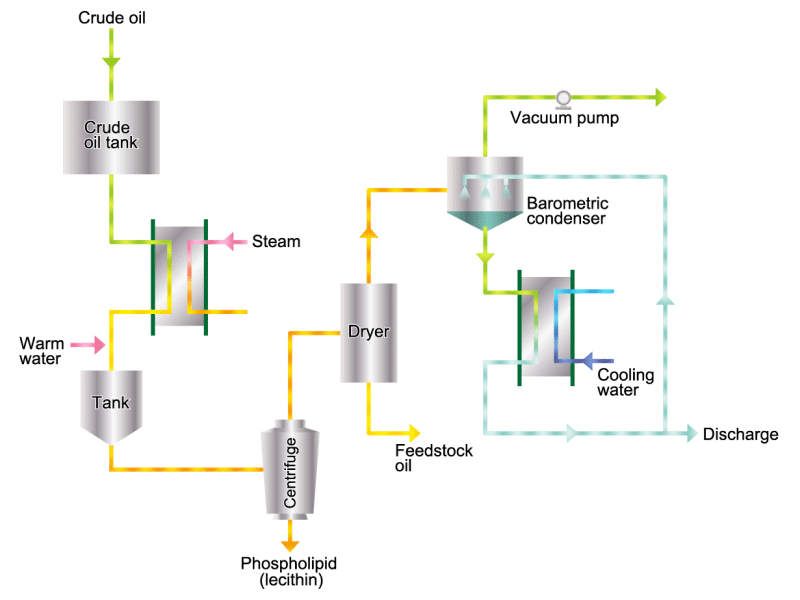
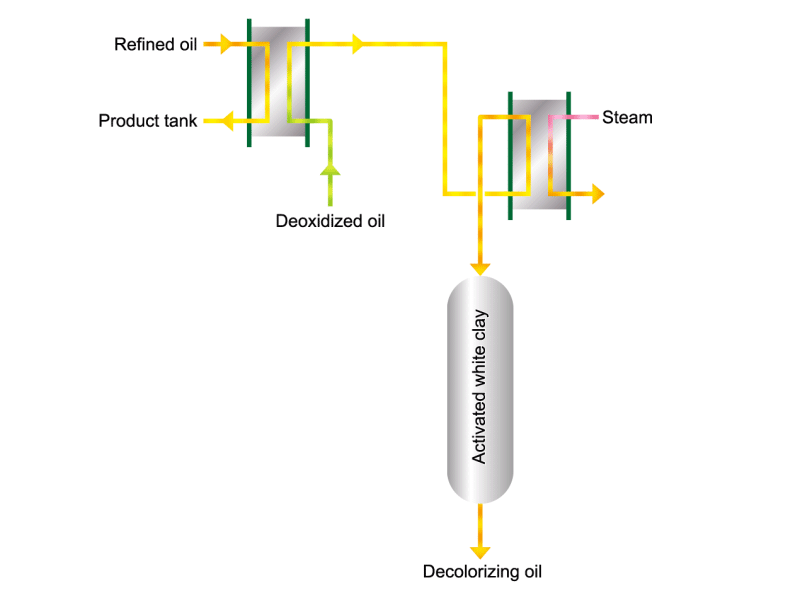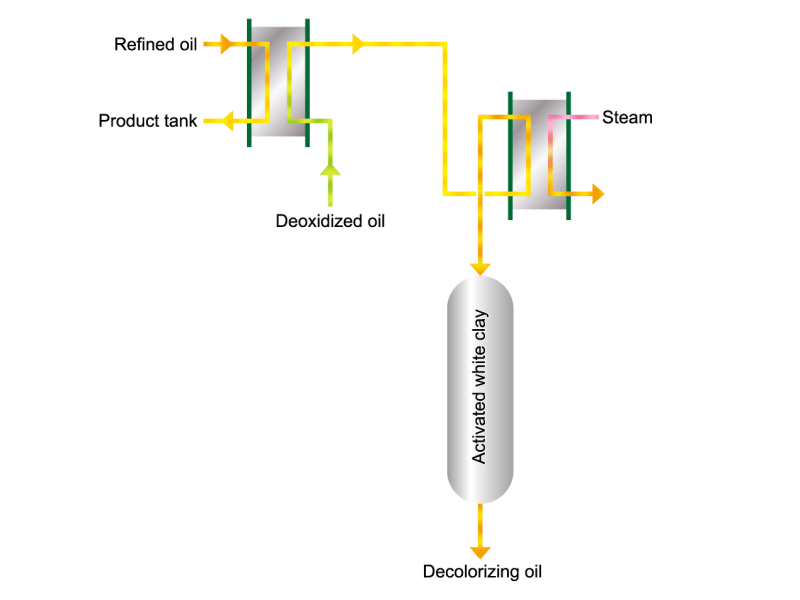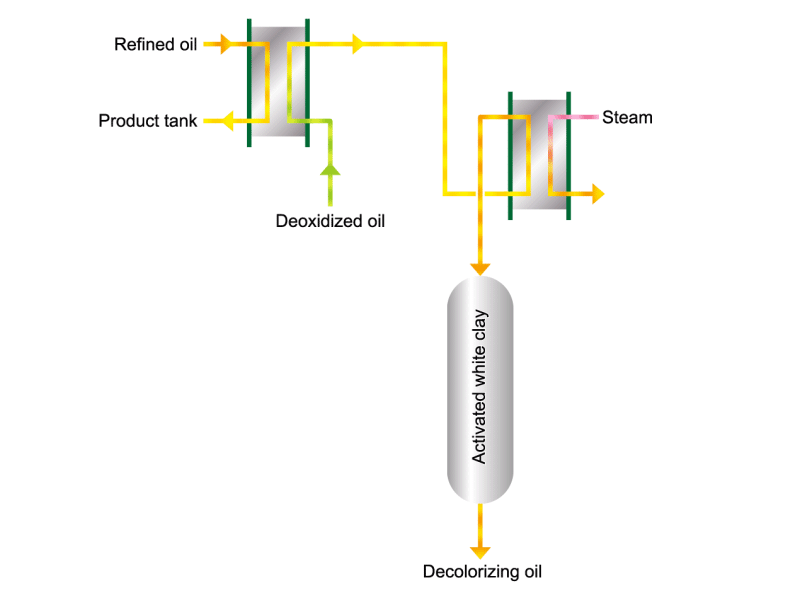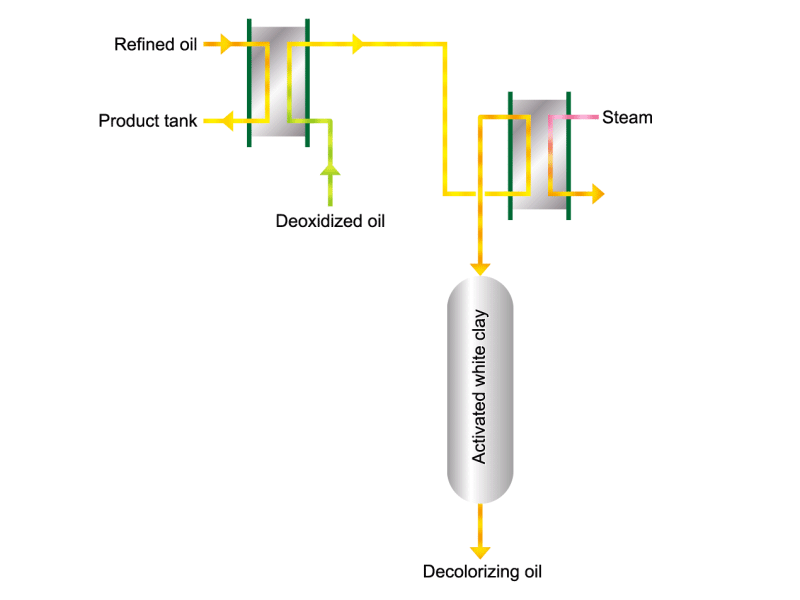
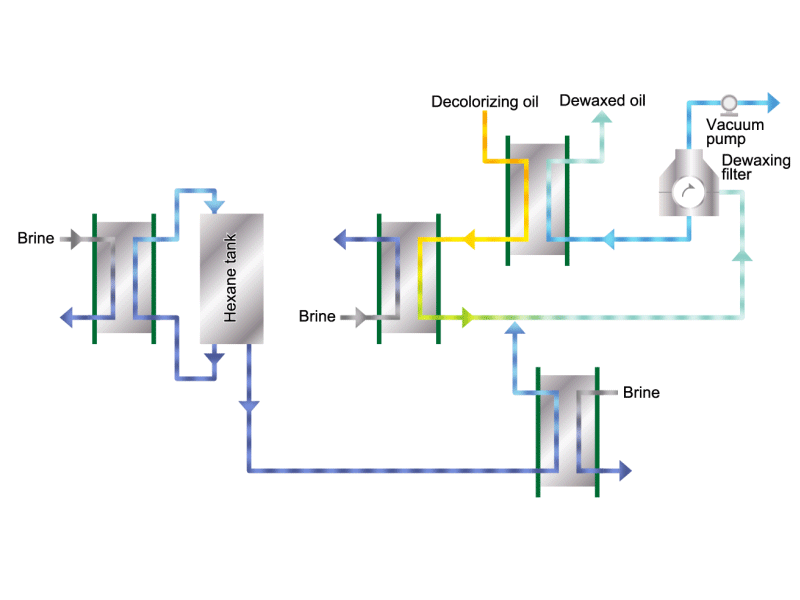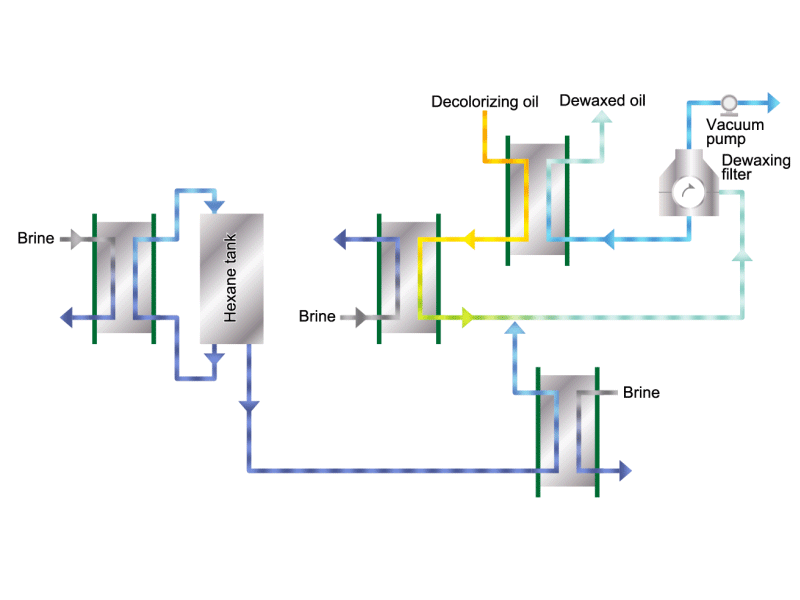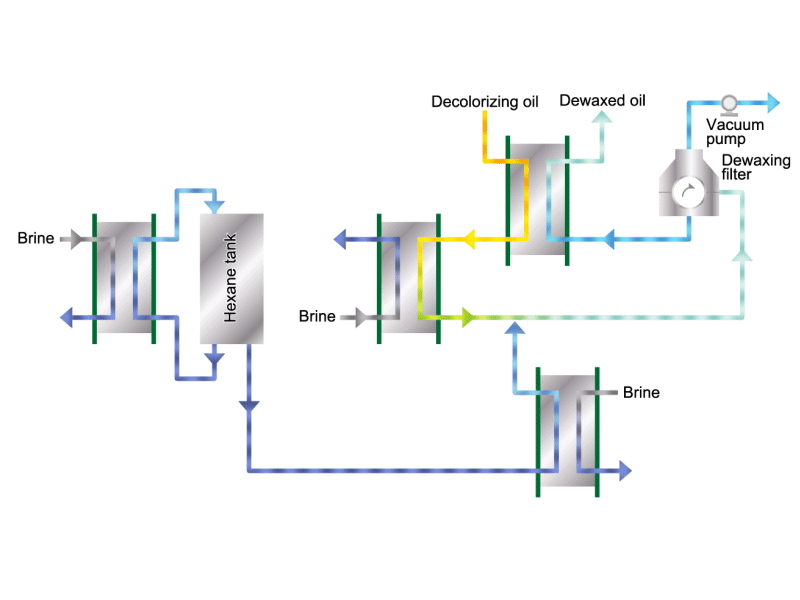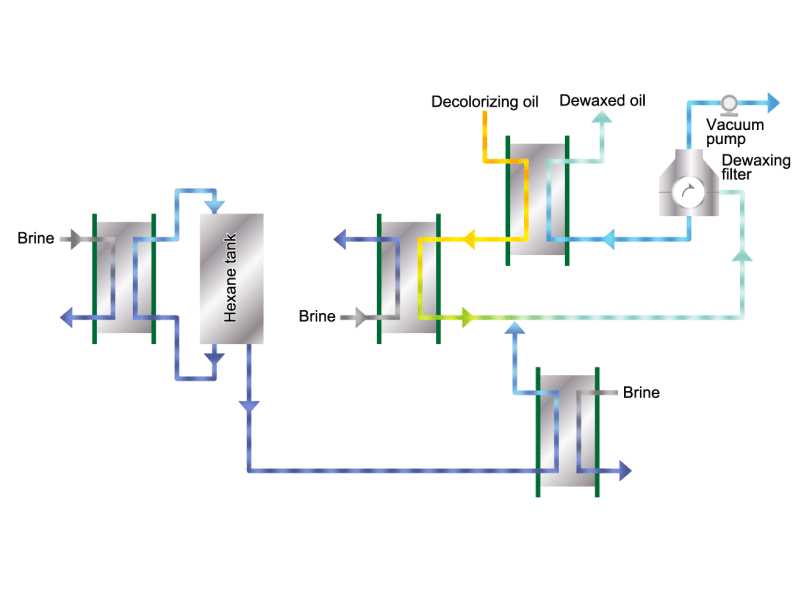
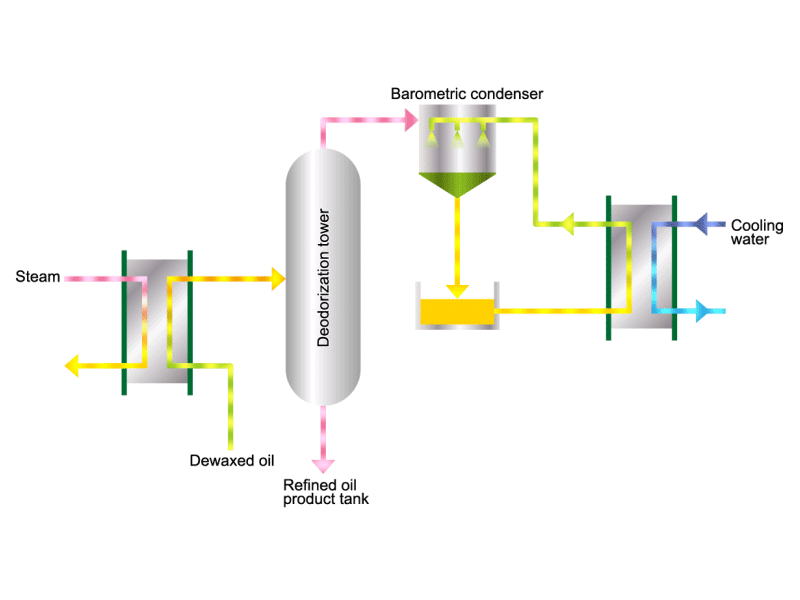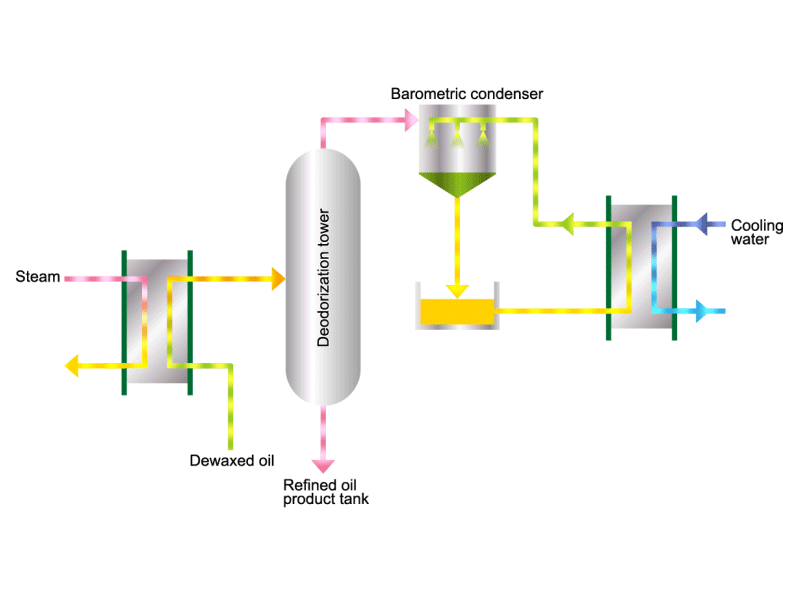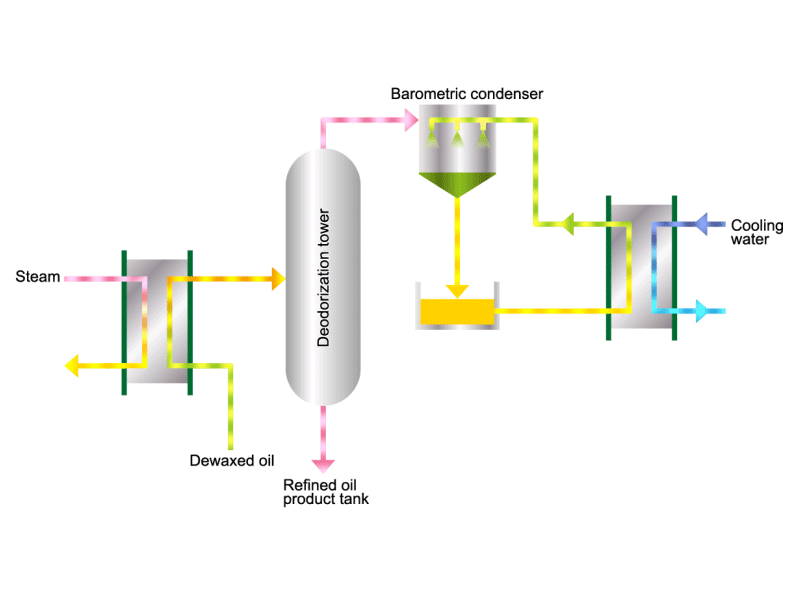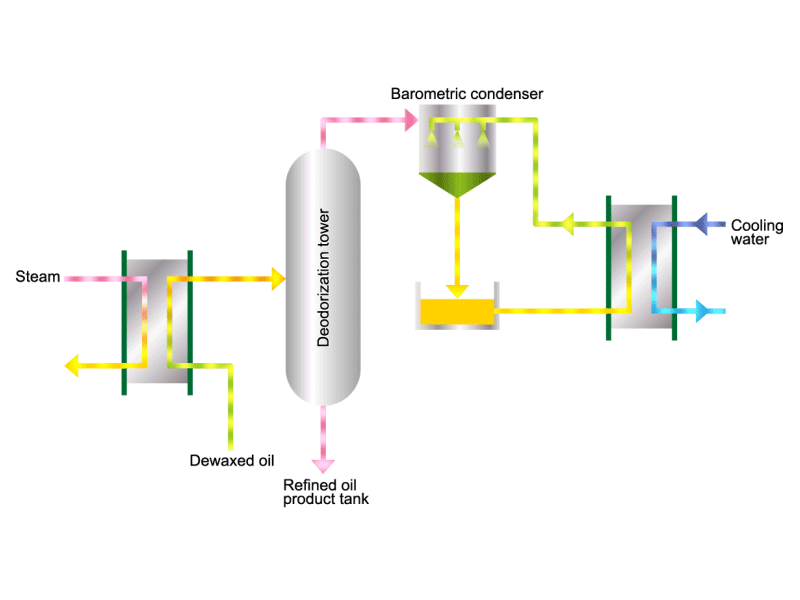
- Cooking oils are made from corn, rapeseed, soybeans, etc. as raw materials. They go through an oil extraction process to extract oil from these raw materials, a refining process to make it suitable for cooking oil, and a manufacturing process of filling containers and transporting products, before the final product is shipped. Cooking oil is popular as salad oil and tempura oil.